BANGKOK, Thailand, Jan 30 (IPS) – Quadrupling in measurement since 1950, the working age inhabitants in Asia and the Pacific now accounts for 67.2 per cent of the full inhabitants within the area and is ready to peak at 3.3 billion by the mid-2030s.
Now could be the second for Asia and the Pacific to harness this demographic window by investing in a extra resilient working age inhabitants.
In Asia and the Pacific, the challenges loom massive. Two in three employees are in casual employment. In the event that they fall sick, lose a job, have a incapacity or grow to be outdated, they don’t have any employment safeguards or social safety to navigate such disruptions and life contingencies.
Half the area’s workforce survives on $5.5 a day, barely sufficient to raise them out of, or defend them from sliding into, poverty. Unpaid care and home employees, are notably weak as they lack entry to earnings and social safety.
A extra resilient workforce is a crucial step in the direction of eliminating poverty. Efficient social safety can mitigate the necessity of households to resort to measures equivalent to taking a baby out of college or promoting livestock. Essential components to foster extra resilient populations embrace extra complete and inclusive social safety techniques and enhanced entry to respectable employment.
Common non-contributory social safety schemes can be certain that all individuals have entry to primary earnings safety to climate disruptions throughout the lifecycle to allow an sufficient way of life.
Entry to common schemes would additionally mitigate the chance of the working age inhabitants falling into poverty, notably casual employees, individuals with disabilities, ladies or migrant employees.
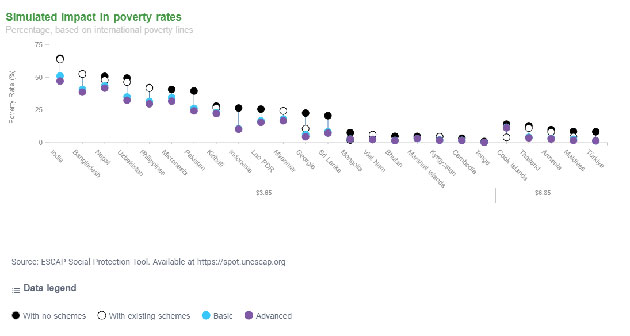
ESCAP simulations present that the mixed affect of investing in a common youngster, incapacity, maternity and outdated age profit can cut back poverty by as much as 91.2 per cent on the $3.65 Worldwide Poverty Line, and on common lower inequality by 8.8 per cent for 25 international locations within the area, at a price ranging between 5.1 per cent and a pair of.6 per cent of GDP.
Whereas non-contributory schemes guarantee a primary degree of earnings safety, they need to be complemented by job-related contributory schemes to offer extra complete and better ranges of earnings safety. Nevertheless, in two thirds of nations, fewer than half the workforce is contributing right into a scheme.
Tackling this problem requires addressing authorized limitations and incentive buildings, simplifying administrative procedures, strengthening enforcement measures, in addition to enhancing consciousness and illustration of casual employees.
Some constructive measures are being applied, by way of the enlargement of voluntary or obligatory contributory schemes, adjusting eligibility standards or offering pension credit for caregivers.
By serving to to match labour demand and provide, Energetic Labour Market Insurance policies (ALMPs) can help the working age inhabitants to search out respectable and productive work by way of public works, coaching, re-skilling or job-matching. ALMPs shall be vital to smoothen the impacts of traits such because the inexperienced transition, inhabitants ageing and digitalisation, which is able to demand new expertise while phasing out some present ones.
A majority of research on vocational and on-the-job coaching programmes determine elevated employability and earnings for trainees all through the area. In Viet Nam, for instance, ladies who obtained job-training had a 12 proportion level greater wage than untrained men and women.
Nevertheless, most international locations spend on common solely 0.2 per cent of GDP a yr on ALMPs. There’s a urgent have to put money into public employment programmes together with enhancing the amount and high quality of coaching schemes, and improve collaboration with the non-public sector, while working in the direction of formalising jobs and advancing the respectable work agenda.
The impacts of the current COVID-19 pandemic demonstrated the fragility of hard-won improvement beneficial properties. Towards the regular decline of maximum poverty over the previous many years, in 2023, as a result of fallout from the COVID-19 pandemic and value of residing disaster, 47 million persons are anticipated to have fallen into excessive poverty.
Escalating frequency and depth of local weather change-related shocks will add additional strain on populations. Work-related contributory schemes equivalent to unemployment insurance coverage can act as an computerized stabiliser to construct the primary layer of resistance towards these shocks.
Nevertheless, unemployment advantages can be found to a lower than 1 / 4 of the full workforce within the area. Properly designed ALMPs might help folks entry employment alternatives, improve productiveness and enhance earnings. When well-coordinated with social safety techniques, equivalent to within the case of Turkiye, they might help teams in weak conditions entry coaching alternatives wanted to re-engage within the labour market.
Different work-related social safety can even help mitigation measures, for instance by way of directing public works programmes in the direction of mangrove restoration or afforestation efforts.
Constructing the resilience of the working age inhabitants shall be paramount to keep up and progress sustainable improvement in Asia and the Pacific. Via extending multipillar social safety techniques throughout the lifecycle and ALMPs, international locations are investing in a key group to construct resilience to life contingencies, work transitions and local weather change: a workforce that is ready to override these disruptions and break by way of cycles of poverty.
Sayuri Cocco Okada is Social Affairs Officer at ESCAP.
IPS UN Bureau
Follow @IPSNewsUNBureau
Follow IPS News UN Bureau on Instagram
© Inter Press Service (2024) — All Rights ReservedOriginal source: Inter Press Service