 Nasa
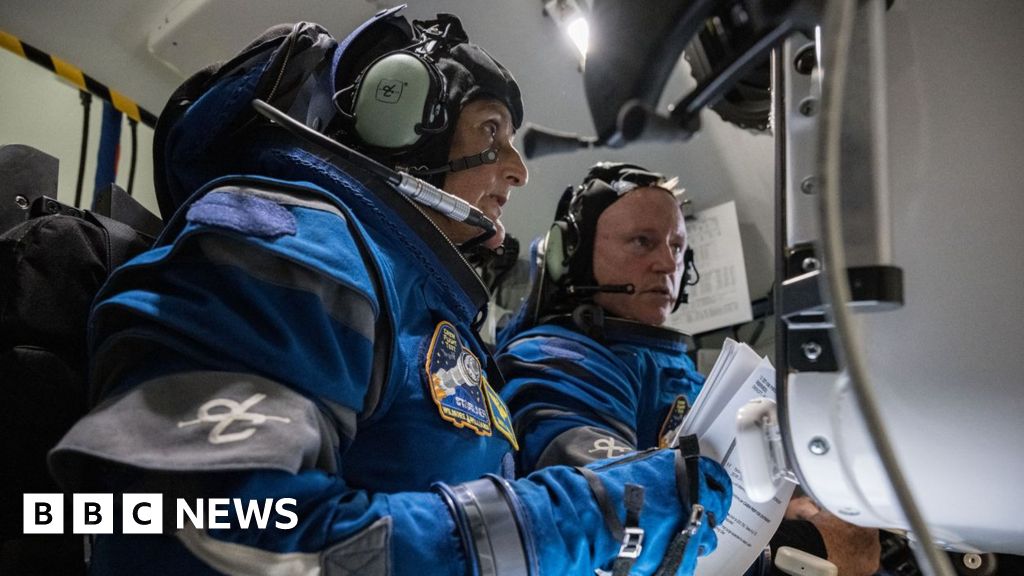
NasaThe 2 astronauts testing out Boeing’s new Starliner spacecraft had been supposed to start making their means again to Earth on Wednesday evening however as an alternative they may keep on the Worldwide Area Station (ISS).
The vessel’s return to Earth had already been delayed because of points with a few of its thrusters and leaks of the helium fuel which pushes gas into the propulsion system.
Nasa is finishing up a high-level evaluation of the technical issues earlier than deciding when to carry its astronauts dwelling.
Suni Williams and Butch Wilmore are in no hazard, however what has gone unsuitable with the spacecraft and what does this imply for his or her journey dwelling?
Starliner was launched on 5 June regardless of their being a small leak of helium fuel. Helium is used to push propellent to the thruster programs used for maneuvering in house and slowing all the way down to renter the Earth’s environment.
The leak was extraordinarily small and engineers believed that it could not have an effect on the mission and so went forward with the launch.
However 4 additional helium leaks developed throughout the mission and 5 of its 28 maneuvering thrusters lower out throughout the method to the house station, 4 of which had been restarted.
The mission was presupposed to have lasted eight days, however the return date was postponed as engineers investigated the problems.
Then on 18 June Nasa introduced that Starliner would begin its journey dwelling at 22:00 EST on Wednesday 26 June (03:00 Thursday 27 June BST).
Nasa had earlier said in a weblog submit stating that the leaks posed no security danger to the astronauts as a result of: “Solely seven hours of free-flight time is required to carry out a traditional finish of mission, and Starliner presently has sufficient helium left in its tanks to help 70 hours of free flight exercise following undocking.”
However only a few days later, following high-level conferences, Nasa concluded that the scheduled return ought to be “adjusted” to a date in July. No further data was given as to why the choice had been modified.
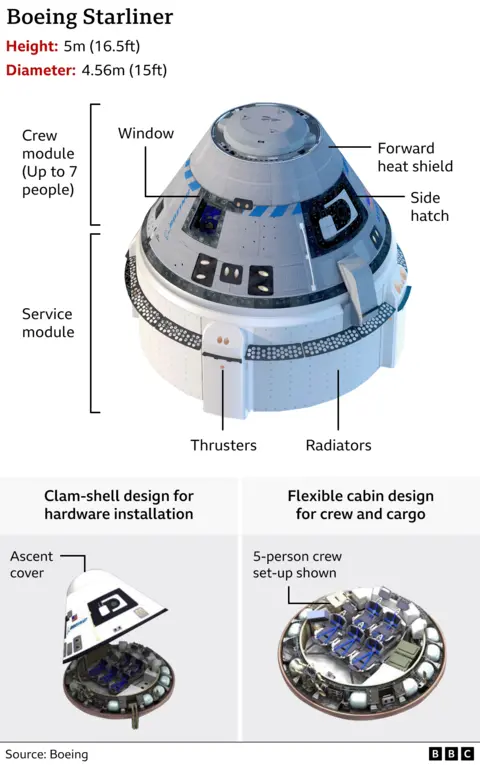
Nasa said that flight engineers wished to check the spacecraft to unravel the faults earlier than it re-entered into the Earth’s environment. That is as a result of whereas the crew capsule will parachute to the bottom, Starliner’s defective decrease ‘service module’ will expend upon re-entry, that means the lack of some data on what went unsuitable.
The house company harassed that the astronauts weren’t stranded and that Starliner was licensed to return to Earth within the occasion of an emergency on the ISS.
What occurs subsequent is topic to a high-level “company stage evaluation” by Nasa to resolve what to do subsequent.
 NASA
NASAThe sequence of occasions raises questions on whether or not the launch ought to have gone forward regardless of the leak.
Dr Adam Baker, who’s head of Rocket Engineering, a UK firm specialising in rocket propulsion programs, says he understands why the launch occurred however says it could have been higher to have gotten to the underside of the reason for the leak and repaired it.
“There’s a danger of attempting to get issues too good and ending up taking too lengthy and it being too costly and consequently, public and political help disappears,” he stated.
“However what I really feel is that they might not have sufficiently thought of the worsening of the leak after launch. That is one thing that Nasa and Boeing in all probability ought to have accomplished.”
That will have been tremendously costly, as it could have concerned taking the rocket off the launch pad and taking the propulsion system out of the spacecraft.
One other difficulty for Nasa’s evaluation is why these points weren’t recognized in any of the 2 earlier uncrewed flight assessments of Starliner, based on Dr Simeon Barber, who’s an area scientist on the Open College.
“The issues now we have seen in the previous couple of weeks are usually not the type we might have anticipated at this stage of the event programme for Starliner,” he says.
“The entire level about this was to check what placing astronauts within the loop of controlling the spacecraft would do by way of efficiency. As a substitute, we appear to be coping with somewhat extra basic points that actually ought to have been ironed out by now.”
 Boeing
BoeingLastly, for Nasa, there’s the vital difficulty of figuring out the underlying reason behind the helium leaks and thruster issues. Till they try this, all of the analyses of the dangers of a secure return of the astronauts and any contingency plans can be incomplete, based on Dr Barber.
“Except the basis trigger is known, they’re having to make a judgement concerning the return based mostly on incomplete data. If you happen to don’t absolutely perceive the reason for any failure then you may’t say for positive that you haven’t obtained a scientific downside that can have an effect on not simply the first propulsion system, but in addition the back-ups.”
As a final resort, Nasa and Boeing can return their astronauts on SpaceXs Dragon capsule, which might be vastly embarrassing for Boeing. However we aren’t in that territory but, based on Dr Baker.
“With new spacecraft you need to count on the sudden,” he says. “That is a wholly anticipated bump within the street and I don’t suppose it to be a significant concern, aside from it must be analysed and stuck earlier than the following crewed flight.”




