Jonathan Amos,Science correspondent, @BBCAmos
 NASA/ESA/CSA/STScI/Brant Robertson et al
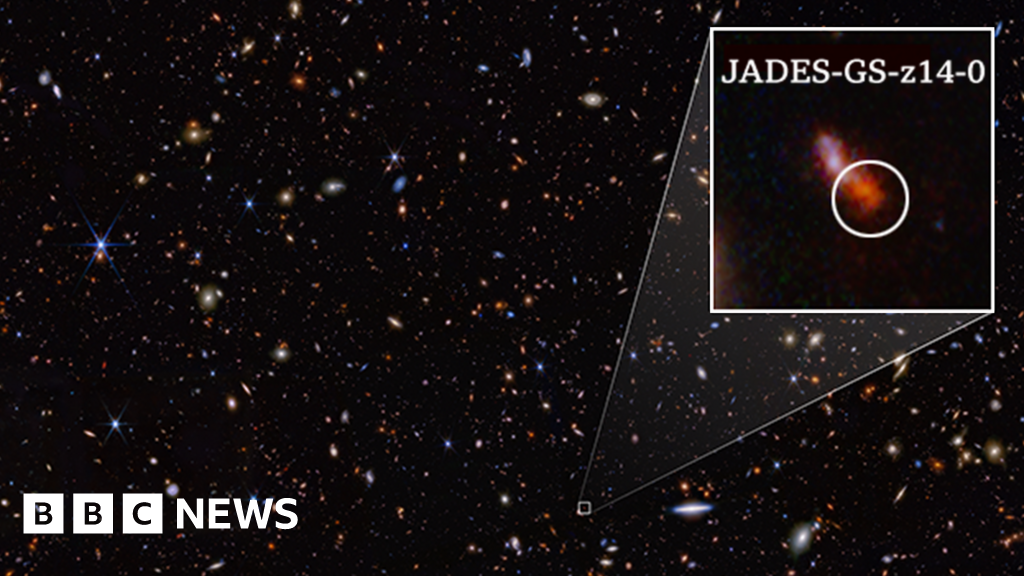
NASA/ESA/CSA/STScI/Brant Robertson et alThe James Webb House Telescope has smashed its personal report for detecting probably the most distant recognized galaxy.
Referred to as JADES-GS-z14-0, the gathering of stars was spied because it was a mere 290 million years after the Massive Bang.
Put one other method – if the Universe is 13.8 billion years outdated, it means we’re observing the galaxy when the cosmos was solely 2% of its present age.
Webb used its large 6.5m-wide major mirror and delicate infrared devices to make the invention.
The telescope’s previous record holder was a galaxy seen at 325 million years after the Massive Bang.
Astronomers say probably the most attention-grabbing facet of the most recent statement will not be a lot the nice distance concerned – as wonderful as that’s – however slightly the scale and brightness of JADES-GS-z14-0.
Webb measures the galaxy to be greater than 1,600 gentle years throughout. Lots of the most luminous galaxies generate the vast majority of their gentle by way of gasoline falling right into a supermassive black gap. However the scale of JADES-GS-z14-0 signifies that isn’t the reason on this case. As a substitute, the researchers imagine the sunshine is being produced by younger stars.
“This a lot starlight implies that the galaxy is a number of a whole bunch of thousands and thousands of occasions the mass of the Solar! This raises the query: how can nature make such a vibrant, large, and huge galaxy in lower than 300 million years?” mentioned Webb astronomers Stefano Carniani and Kevin Hainline.
Dr Carniani is affiliated to Scuola Normale Superiore in Pisa, Italy, and Dr Hainline is from the College of Arizona in Tucson, Arizona.
The $10bn James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) was launched in 2021 as a joint endeavour of the US, European and Canadian house businesses.
It was designed particularly to see farther throughout the cosmos – and additional again in time – than any earlier astronomical instrument.
Certainly one of its key targets was to search out the very first stars to ignite within the nascent Universe.
These big objects, maybe many a whole bunch of occasions the mass of our Solar, had been made solely of hydrogen and helium.
They’re theorised to have burnt sensible however transient lives, forging of their nuclear cores the heavier chemical parts recognized in nature at this time.
In JADES-GS-z14-0, Webb can see a major quantity of oxygen, which tells researchers the galaxy is already fairly mature.
“The presence of oxygen so early within the lifetime of this galaxy is a shock and means that a number of generations of very large stars had already lived their lives earlier than we noticed the galaxy,” added Drs Carniani and Hainline.
The “JADES” within the object’s title stands for “JWST Superior Deep Extragalactic Survey”. It’s considered one of various statement programmes utilizing the telescope to probe the primary few hundred million years of the cosmos.
“z14” refers to “Redshift 14”. Redshift is the time period astronomers use to explain distances.
It is primarily a measure of how the sunshine coming from a far-off galaxy has been stretched to longer wavelengths by the growth of the Universe.
The better the space, the better the stretching. The sunshine from the earliest galaxies is stretched from ultraviolet and visual wavelengths into the infrared – the a part of the electromagnetic spectrum to which James Webb’s mirrors and devices had been particularly tuned.
“We may have detected this galaxy even when it had been 10 occasions fainter, which implies that we may see different examples but earlier within the Universe – most likely into the primary 200 million years,” mentioned Prof Brant Robertson from the College of California at Santa Cruz.
The JADES discovery and its implications are described in a quantity scholarly papers revealed on the arXiv preprint service.




